Joomla User Manual
Manual Index
File Permissions: Linux
Introduction
The following information is for Linux based servers. If your web server is a Microsoft Windows based server(IIS), you should see Permissions: Windows.
Depending on the security configuration of your Web server the recommended default permissions are:
- 755 for directories
- 644 for files
- 444 for the
configuration.phpfile (when a Global Configuration change is saved Joomla first changes the permission to 644, saves the change and then changes the permission back to 444)
Never use 777 unless you know what you are doing! Do not use extensions that require 777 permissions!
How to Locate the Permissions
There are a variety of methods available to view and change the permissions of website files or folders. The host control panel file browser or a common File Transfer Protocol (FTP) program should each provide a method to see and change file and folder permissions. The command line is good for those who have terminal access and familiarity with system commands.
Depending on what you are using, you should see something like this image of part of the Joomla root file system as seen in cPanel:
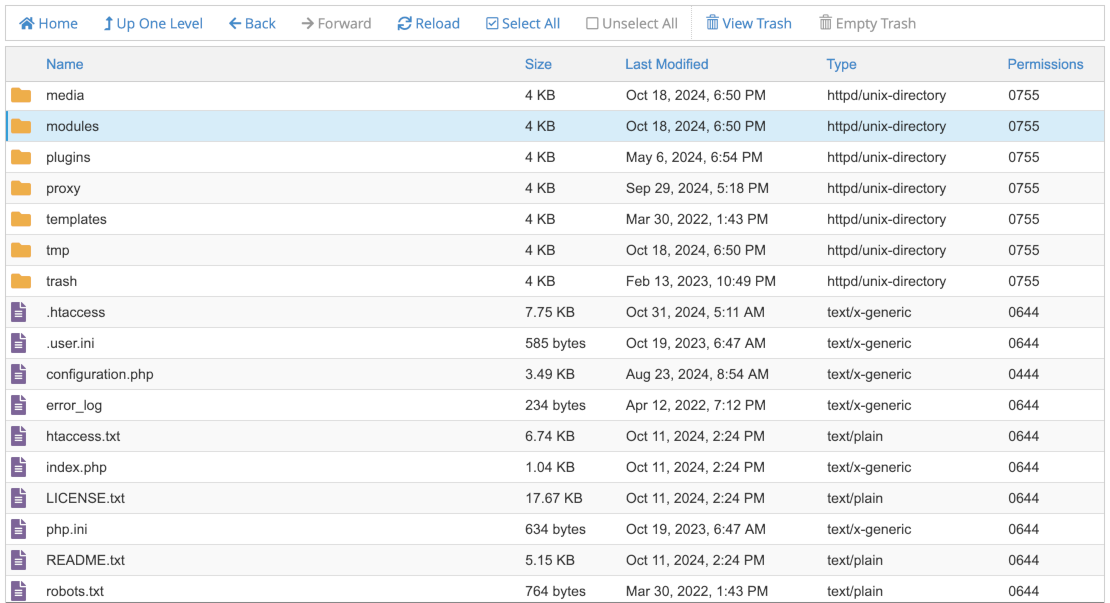
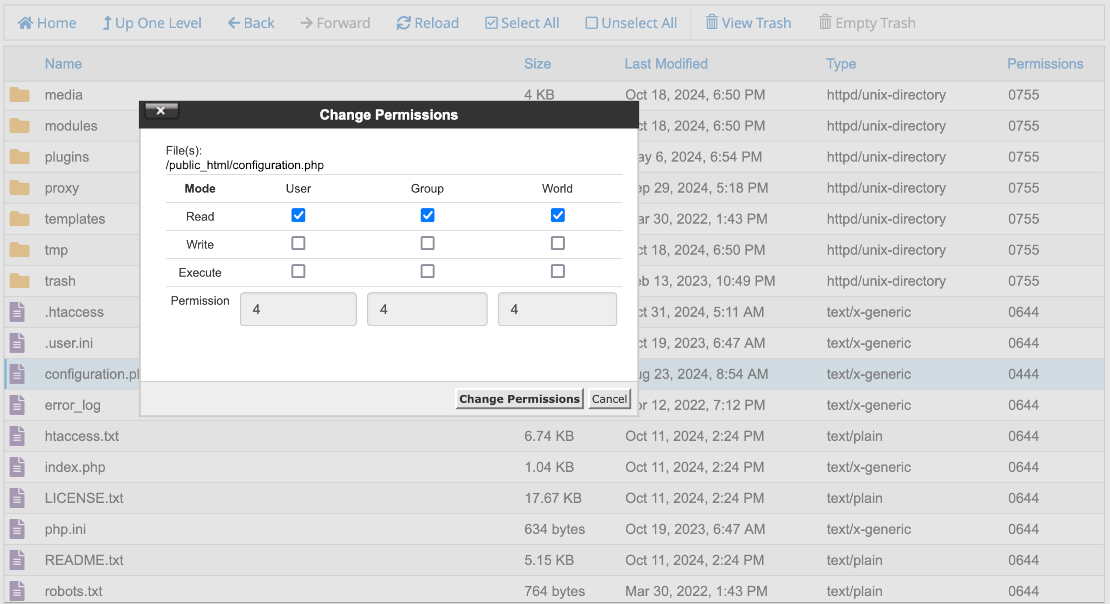
The permissions are at the far right and preceded by a zero to indicate that they are octal numbers. There should be a form to change the permissions of one or more selected items:
In a terminal window, file and folder permissions are displayed as letter
groups rather than numbers (the leading d indicates the item is a directory):
drwxr-xr-x 20 ceford staff 640 14 Oct 22:23 components
-r--r--r-- 1 ceford staff 3485 27 Oct 06:56 configuration.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 ceford staff 64 20 Oct 14:21 files
-rw-r--r-- 1 ceford staff 6899 30 Sep 09:27 htaccess.txt
drwxr-xr-x 15 ceford staff 480 24 Oct 12:19 images
Permission Numbers
In a permissions display of the form 777, each octal digit corresponds to three letters for three different user groups:
- First digit = owner (the item owner -
cefordin the command line list above) - Second digit = group (the group allowed access -
staffin the list above) - Third digit = others (everyone else on this computer)
Meaning of the numbers
Each octal digit is the sum of the permissions granted:
r = Read = 4
w = Write = 2
x = Execute = 1
Add the numbers for each permission required for a given user group:
| "Octal" # | (r)ead | (w)rite | e(x)ecute | User or Group or Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | no | no | no | --- 0+0+0 = 0 |
| 1 | no | no | yes | --x 0+0+1 = 1 |
| 2 | no | yes | no | -w- 0+2+0 = 2 |
| 3 | no | yes | yes | -wx 0+2+1 = 3 |
| 4 | yes | no | no | r-- 4+0+0 = 4 |
| 5 | yes | no | yes | r-x 4+0+1 = 5 |
| 6 | yes | yes | no | rw- 4+2+0 = 6 |
| 7 | yes | yes | yes | rwx 4+2+1 = 7 |
Examples
- 755 is rwx (owner), r-x (group) and r-x (others) or in other words
everyone may read and execute (run) but only the owner(you) may make
changes to the file. It would look like this when it is all put
together:
-rwxr-xr-x. This is the normal setting for folders. - 644 is rw-, r--, r-- or EVERYONE can read the file but only the owner
may write to the file or
-rw-r--r--. This is the normal setting for files. - 777 or
-rwxrwxrwxmeans EVERYONE can read, write and execute ANY fileThis is something you **NEVER** want to allow on your server/website unless you are absolutely sure you know what you are doing.
Permissions are used for directories as well as files, which is why you
might see this drwxr-xr-x where the d is for directory.
For a complete explanation read the Wikipedia article on Filesystem permissions