Joomla User Manual
Manual Index
Global Configuration
Overview
On installation, a Joomla site creates a file named configuration.php in the root of the site. This file contains the values of configuration variables that apply to the site as a whole. Examples include the site name and database credentials that were entered during the installation process. There are many more variables that are given suitable initial values.
The Global Configuration form allows a Super User to change the configuration variables to suit the needs of the site. In addition to the variables stored in configuration.php, the form keeps track of Logging, Filtering and Access Control information, some of which is stored in the database.
Screenshot
The Global Configuration form has six tabs some of which have long lists of parameters. Use the Toggle Inline Help button in the Toolbar to see more or less information on each parameter.
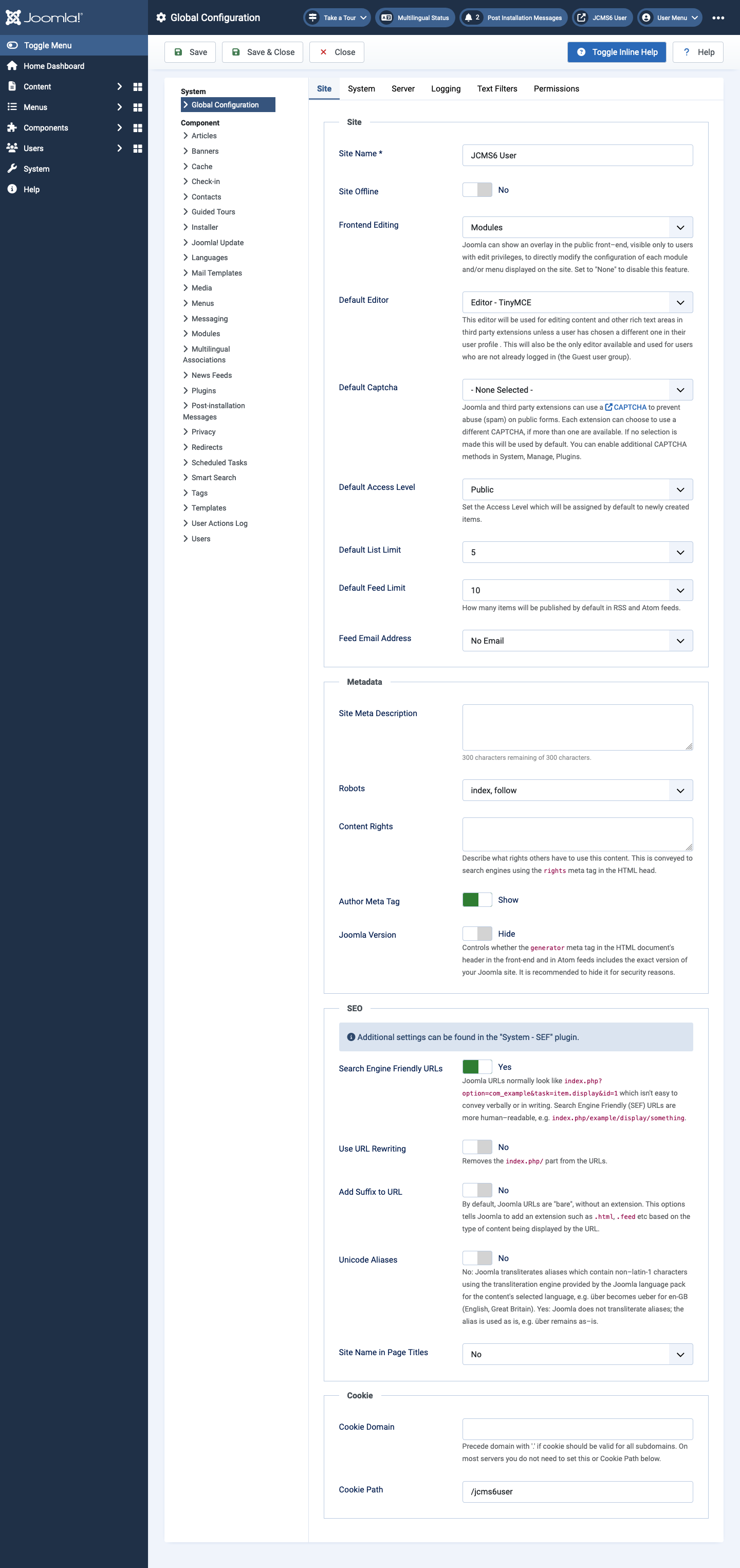
Some parameters show or hide other parameters when selected. For example, the Site Offline button shows more fields when set to Yes than it does when set to No. With inline help expanded most fields are sufficiently well documented to need no further explanation here, other than some additional user notes on each tab.
Site tab
Site panel
- Site Name This is the name of the site that appears in the Administrator login form and in the Site link in the Title bar. Change it as required.
- Site Offline There is a separate tutorial on this item.
- Default List Limit sets the default maximum number of items per page in list views. By default, this parameter is set to 20 but list views usually include a drop-down list to select other values ranging from 5 to 100. Fewer values are quicker to process and involve less user scrolling.
Metadata panel
- Site Metadata Description This is the default metadata description used if such a description is not specified in an article Meta Description field or a menu Meta Description field. If all three are empty the metadata description is omitted from the page output. Search engines often use this to provide descriptive text for a page. If absent, search engines my use text from the content of the page, which may be inappropriate. A description of the purpose of the site of around 20 words is recommended.
- Content Rights sets the rights metadata entry. If appropriate, describe here what rights others have to use this content. This metadata entry is omitted from web pages if this entry is blank. Example: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (see the Creative Commons Licence Chooser).
SEO panel
SEO is an acronym for Search Engine Optimisation. Settings in this group alter the format of URLs for pages in the website and this may have a significant effect on the search rankings of individual pages and the site as a whole. SEO URLs are more human-readable.
Tip After making any changes to the settings in this group, refresh any of the website's pages already open in your web browser (usually Ctrl+R or Cmd+R will do this). Failure to refresh may mean that the format of web links internal to the site no longer match that which Joomla is expecting and thus give the appearance of broken links.
Tip If at all possible, avoid altering the SEO Settings once a website is established. Doing so may result in broken links from other sites and perhaps a temporary drop in search engine rankings.
- Unicode aliases Changing this parameter does not retroactively change aliases, it just changes the behaviour of automatic alias generation for future content editing and creation. Transliteration (No) is the default setting.
Cookie panel
- Cookie Domain Overrides the site's default cookie domain with the
domain added here. The most likely situation when this would be needed
is when the Joomla site is “bridged“ with other sites (e.g. forum or
e-commerce) in sub-domains of the Joomla site. The default cookie
domain may be like
www.example.com, but using.example.com(note the leading dot) here will deliver cookies valid for any sub-domain of example.com. - Cookie Path Overrides the site's default path for which the cookie is valid with the path added here. This may be needed if you have several Joomla installations in sibling folders.
System tab
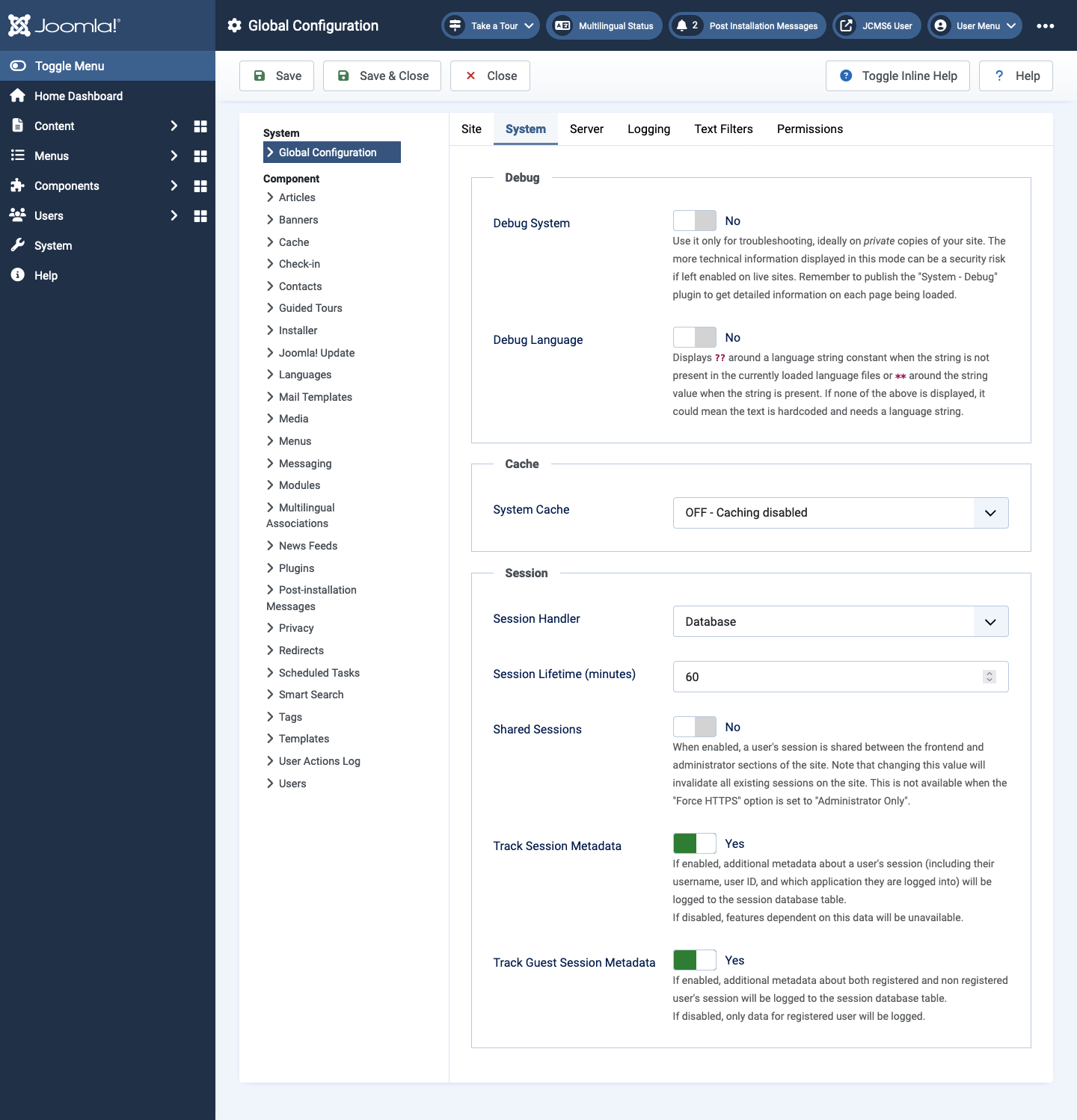
Debug panel
The items in this panel are well explained by the inline help. However,
if you encounter a problem that disables normal access to the
Administrator interface you may need to set Debug System by editing
configuration.php with a text editor. On most Linux based hosting
systems the file permissions are set to 444 which prevents saving from a
text editor. Change the permission to 644 before editing. Then set
$debug = true; and set $error_reporting = 'maximum'; and save. You
should then get a stack trace identifying exactly where the problem
occurs. You can use that to seek help in the Forums. Most problems arise
from incompatible third party extensions or from problems with the
hosting environment.
Server tab
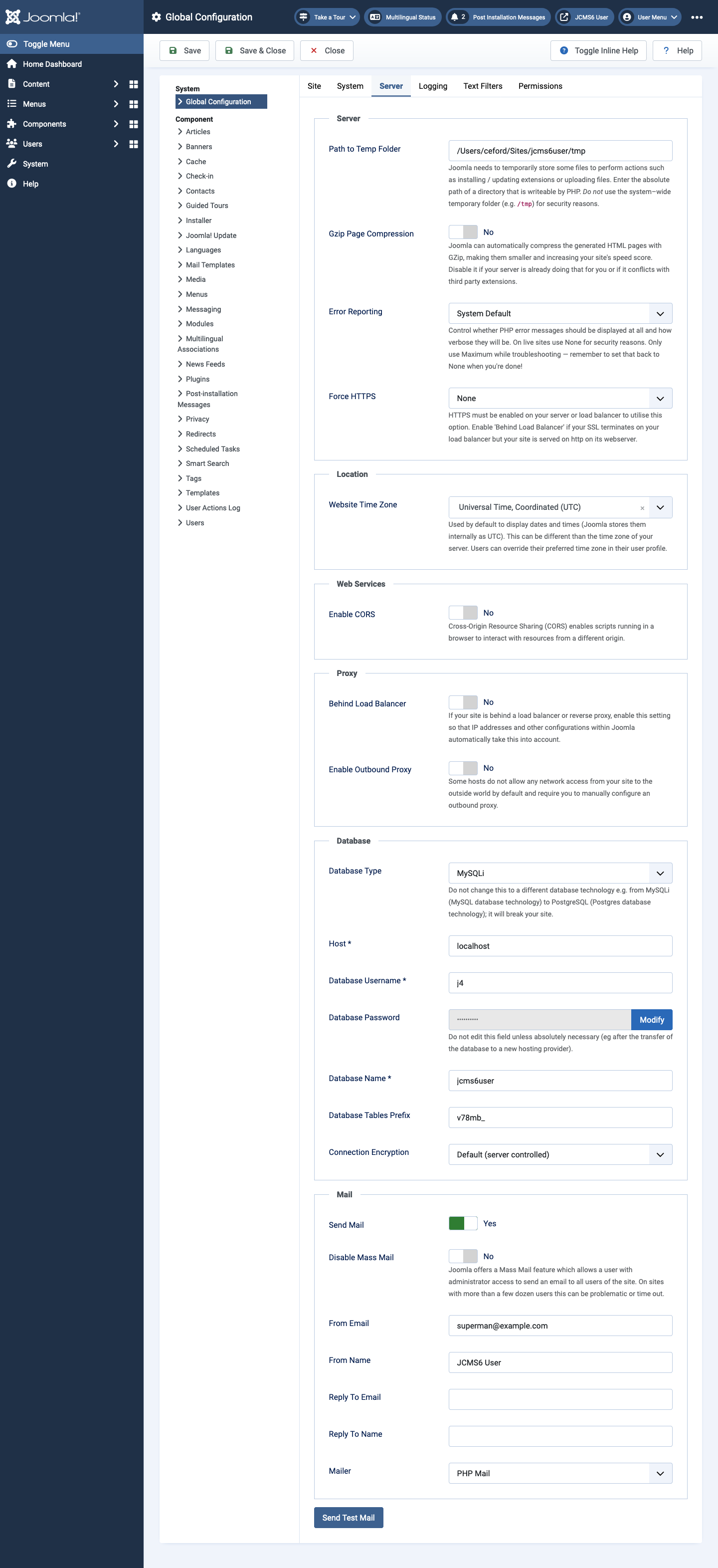
Mail panel
A Joomla site should be able to send outgoing emails. Amongst other things, it will send automated messages to the site owner when updates are available. However, some hosting services restrict methods by which outgoing mail may be sent.
Send Test Email
Prior to Joomla 5.3, the Send Test Mail button sent a message to the address configured in the From Email field. Since 5.3 the test mail is sent directly to the email address of the logged-in administrator.
- Try PHP Mail first and select the Send Test Mail button. If the email arrives you are good to go. Otherwise:
- Try the Sendmail option. If that does not work:
- Try the SMTP option. This needs to be set up for a specific mail server. It could be one provided by your hosting service. It could be a GMail account.
- SMTP Host The hostname of the SMTP server (e.g. smtp.example.com).
- SMTP Port The port to use when connecting to the SMTP server. This will usually be 25 when SMTP Security is set to None, or 465 or 587 when SMTP Security is set to
SSL/TLSorSTARTTLS. Ask your SMTP service provider which port to use. - SMTP Security The form of security required by the SMTP server: None, SSL/TLS or STARTTLS. The default is None.
- SMTP Authentication Whether or not the external SMTP server requires authentication before accepting outgoing emails. The default is No.
- SMTP Username The username to be used when connecting to the SMTP server in SSL or TLS mode. May be left blank if there is no SMTP authentication.
- SMTP Password The password to be used when connecting to the SMTP server in SSL or TLS mode. May be left blank if there is no SMTP authentication.
- SMTP Port The port to use when connecting to the SMTP server. This will usually be 25 when SMTP Security is set to None, or 465 or 587 when SMTP Security is set to
Using Gmail as Mail Server
If you have a working Gmail account you can use Gmail as your mail server by setting it in the global configuration. On the server tab set the following:
- Mailer: SMTP
- SMTP Host: smtp.gmail.com
- SMTP Port 465
- SMTP Security: SSL/TLS
- SMTP Authentication: Yes
- Set the next two lines with your information. You need to use an app specific password (ASP), described below.
- SMTP Username: your gmail username
- SMTP Password: the app specific password (ASP) you generated, described below.
The following are also working combinations:
- SMTP Port 587
- SMTP Security: STARTTLS
- SMTP Port 25
- SMTP Security: STARTTLS
Notes
- The SSL module does not need to be enabled in Apache.
- The OpenSSL extension needs to be enabled in PHP. The details can be found at the php.net Installation page.
- If you are using WAMP on Windows, the openssl module is not enabled by
default and you need to enable it. To do this:
- Open the php.ini file and uncomment the line
extension=php_openssl.dllby removing the semicolon ; from the beginning of the line. - Save the php.ini file and restart the Apache service.
- Open the php.ini file and uncomment the line
- If you use 2-step verification in Gmail, you need to add a new password in Settings - Accounts - Change accounts settings - Other Google Account settings - Security - 2-step verification - Manage your application specific passwords.
- When the new Application Specific Password (ASP) is presented in groups of four characters separated by spaces, make sure that you do NOT enter the spaces into the SMTP password in the mail server settings in Joomla.
- Application Specific Passwords (ASPs): See the Google Support page on how to Sign in with App Passwords.
- 2-Step Verification: See the Google Support page on how to Turn on 2-Step Verification.
Logging tab
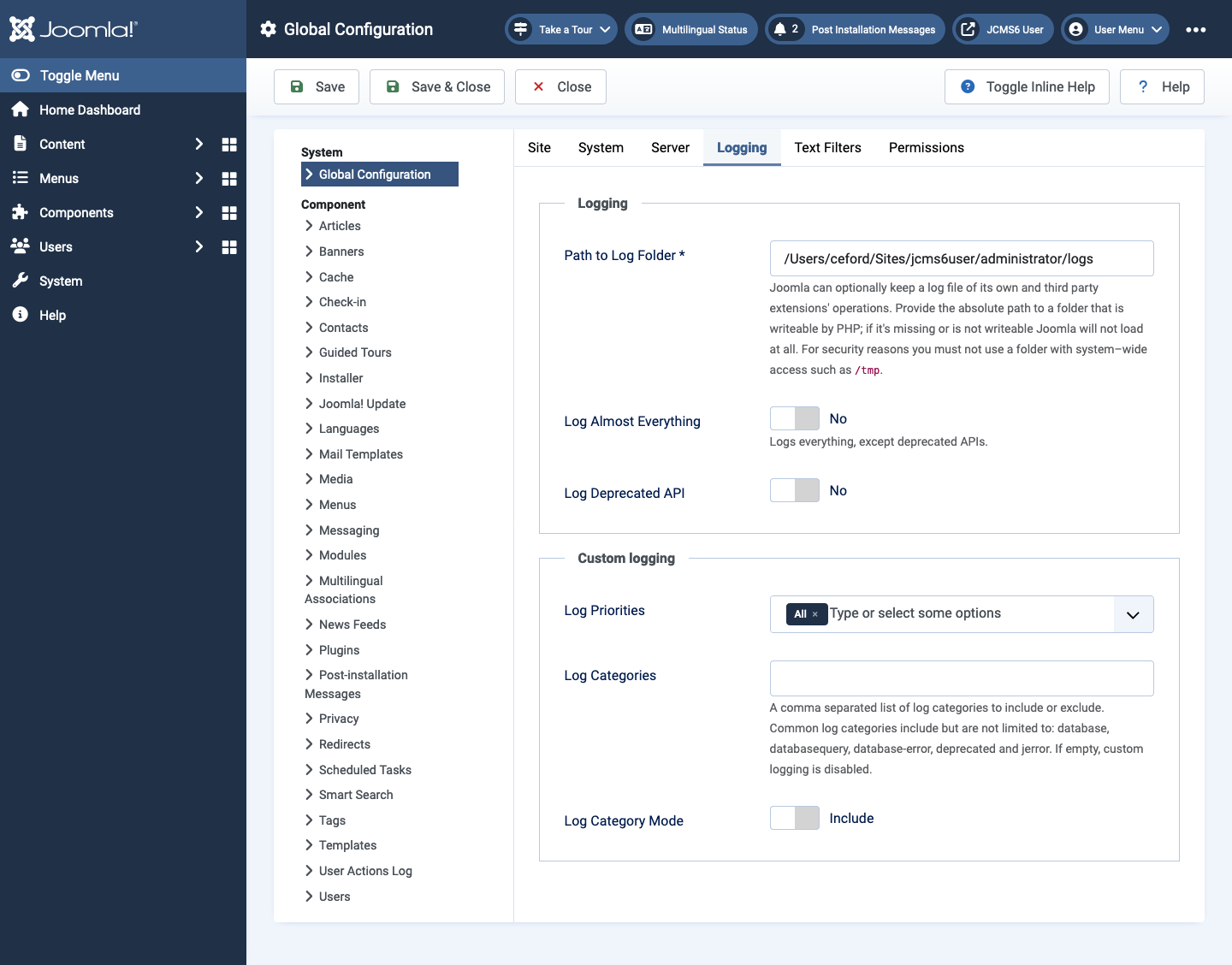
In normal operation a Joomla site should have logging disabled. If there
are problems you can enable logging by setting the Log Almost
Everything field to Yes. The Log Deprecated API is really for
developers only. The Path to Log Folder field shows you where to
look for logs if you have set up logging to help with debugging. The
error logs you find there are only those trapped by Joomla. There may be
other errors that will only appear in your server error logs.
The Text Filters tab
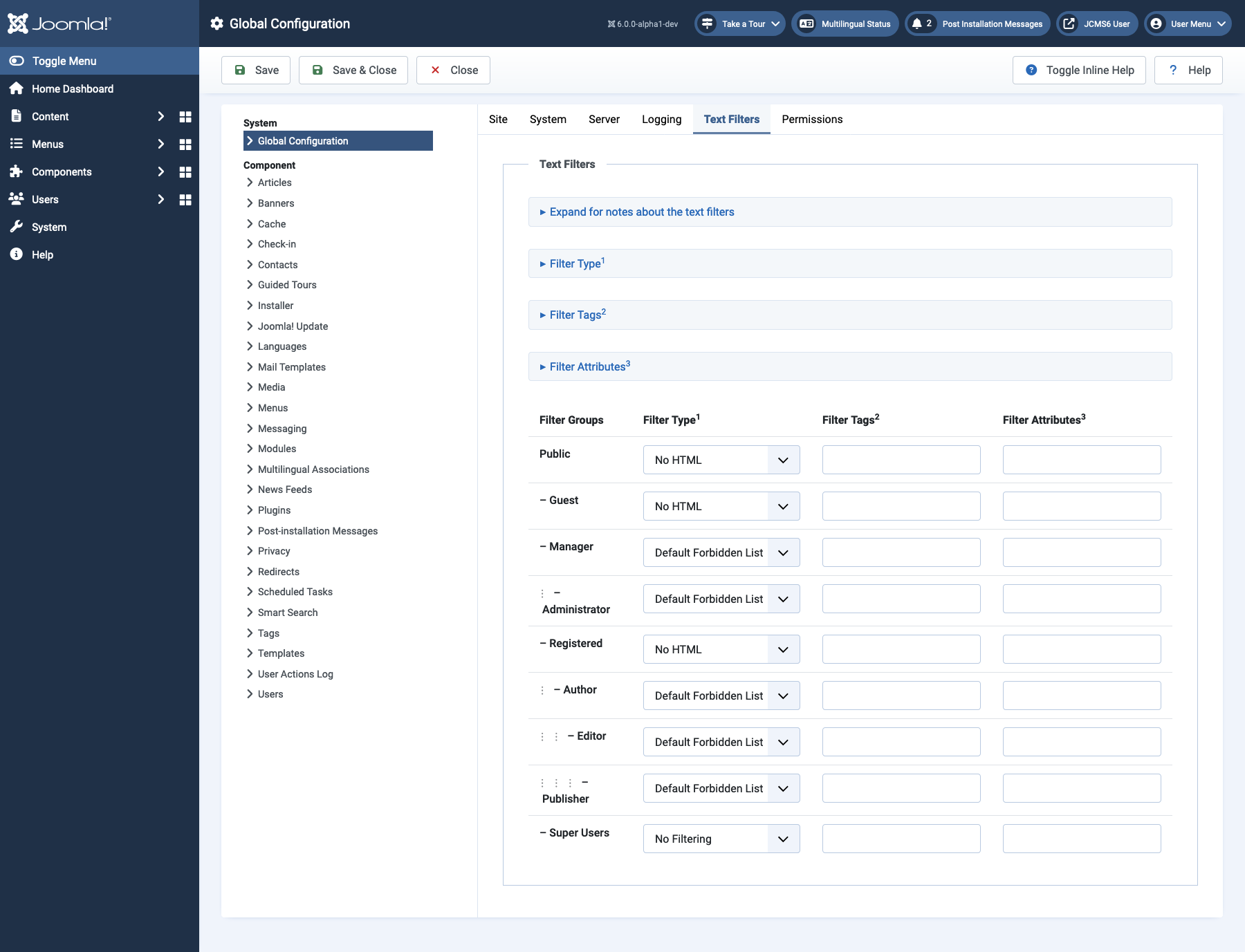
The text filter settings will be applied to all text editor fields submitted by users in the selected groups. These filtering options give more control over the HTML your content providers submit. You can be as strict or as liberal as you require to suit your site's needs. The filtering is opt-in and the default settings provide good protection against markup commonly associated with website attacks.
Permissions tab
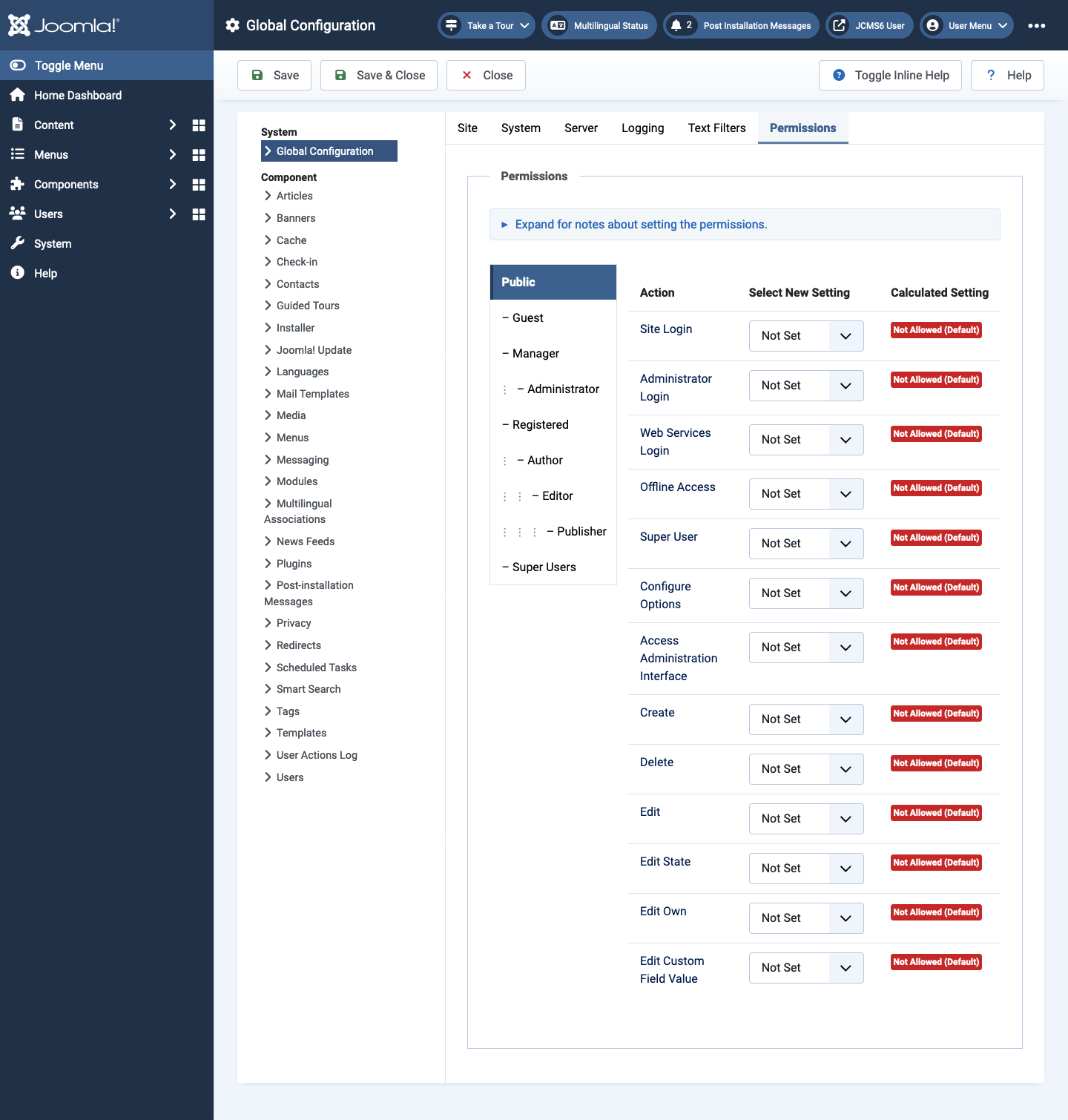
Permissions control what users in each User Group can see and do. The entries in the Permissions tab set the default permissions for the site.
There are comprehensive descriptions of the use of the settings under this tab and the general principles of operation and set-up of permissions in an Access Control List Tutorial.