Joomla User Manual
Manual Index
Article: Edit - Metadata
Introduction
Metadata is information about a web page contained in the first part of the page
between <head>...</head> tags. Most of this information is not seen by site
visitors but it is used by search engines to provide appropriate results for
search requests. So it is in your interests to use informative metadata.
Some of the metadata items are provided by the template in use and you do not need to set them yourself. Common examples:
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<meta name="generator" content="Joomla! - Open Source Content Management">
There are other forms of metadata such as Open Graph Data used by Facebook and schemas used to describe specific types of page such as Person, Place or Product. They are not covered here.
The items of metadata that are often neglected are the page Title, which
occurs within <title>...</title> tags in the page <head>, and the page
Description, which occurs within <meta> tags but may be absent. They
are covered here.
The page Title
An article title is required for any new page. A few guidelines and tips for composing good titles from the Mozilla Developer Network:
- Avoid one- or two-word titles. Use a descriptive phrase, or a term-definition pairing for glossary or reference-style pages.
- Search engines typically display about the first 55–60 characters of a page title. Text beyond that may be lost, so try not to have titles longer than that. If you must use a longer title, make sure the important parts come earlier and that nothing critical is in the part of the title that is likely to be dropped.
- Don't use "keyword blobs". If your title is just a list of words, algorithms often reduce your page's position in the search results.
- Try to make sure your titles are as unique as possible within your own site. Duplicate—or near-duplicate—titles can contribute to inaccurate search results.
Additional recommendations from Google:
- Specify a unique title for every page
- Make your title descriptive of the page content, and concise
- Avoid keyword stuffing (repeatedly using similar words like "Foobar, foo bar, foobars, foo bars")
- Avoid using generic titles - each page should have an unique title, ideally dynamically updated in relation to the content being displayed
- Brand your titles, but do it concisely and in relation to the content being served
There are various Webmaster Tools which can be used to identify if there are problems with your listings in a particular search engine - it is always worth paying attention and correcting any problems. One example:
Google support article on using titles for your web pages
In Joomla, for a single page the article title becomes the page title used in the head and displayed in the browser tab. For a composite page, such as Featured Articles or a Category blog, the menu item Title becomes the page title. So you need to put some thought into composition of good descriptive titles for both articles and menu items.
The page Description
The article Meta Description is a field in the Publishing tab of the article data entry form:
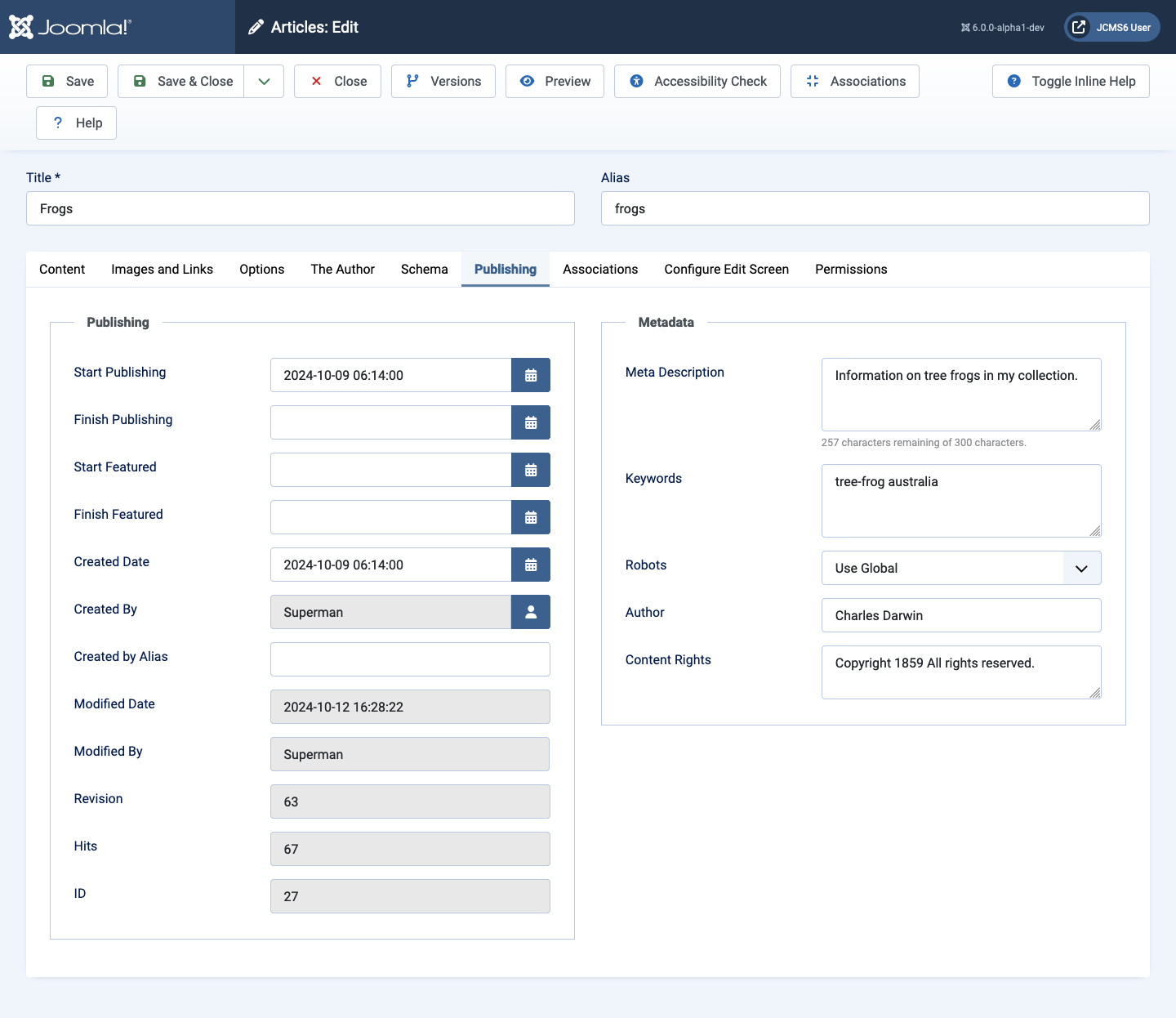
If there is no article metadata description then a single article menu item metadata description will be used if it is set. If there is no menu item metadata description then the global site meta description is used if it is set. Otherwise the metadata description field is omitted.
Google recommends the following to ensure that you gain the most from your search engine indexing:
- Ensure every page has unique, relevant meta descriptions
- Ensure you apply metadata for listing pages (e.g. blog & list layouts) in addition to individual articles - this is commonly overlooked on Joomla! websites
- Include factual information if relevant (e.g. blog articles may include the author, products might include the price or manufacturer)
- Consider using automatically generated metadata - but make sure it is relevant, readable and accurate.
- Make your descriptions descriptive!
Another reference:
Google support article on using metadata
Keywords
Once upon a time, Search Engines used keywords to help classify content. So authors stuffed their keywords metadata with vast numbers of keywords hoping to increase their SEO ranking. And in response Google stopped using keywords for ranking purposes. Search the web for advice and you will find some sources say not to bother and others saying they still have value.
Keywords are not use by Joomla core. If in doubt, don't bother.
Robots
The default value of Use Global does not put a meta tag in the HTML page head.
Other values do. There is a robots.txt file in the root of the Joomla site.
If you wish to control robots you should read this file. It has an explanation
of how to use it
Author
You could enter the formal name of the Author to appear as metadata.
Rights
You could enter a Copyright notice to appear as metadata.
Example metadata
This is what the metadata looks like in the article source view:
Here is an example of the content of the <head> after completion of all of
the metadata fields:
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="rights" content="Charles Darwin © 1859">
<meta name="author" content="Charles Darwin">
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<meta name="description" content="Publicity for The Origin of Species.">
<meta name="generator" content="Joomla! - Open Source Content Management">
<title>Publicity</title>
Note that the keywords output field is absent.