Joomla Developer Manual
Manual Index
HTTP Headers
Introduction
Joomla 4 introduced an HTTP Header system designed to help site owners configure HTTP Security Headers. It is implemented using a System - HTTP Headers plugin. There is a comprehensive User tutorial on this topic. This tutorial is shorter and covers some points relevant for developers.
The System - HTTP Headers Plugin
Plugin tab
Navigate to System → Plugins → System - HTTP Headers to access the plugin configuration form.
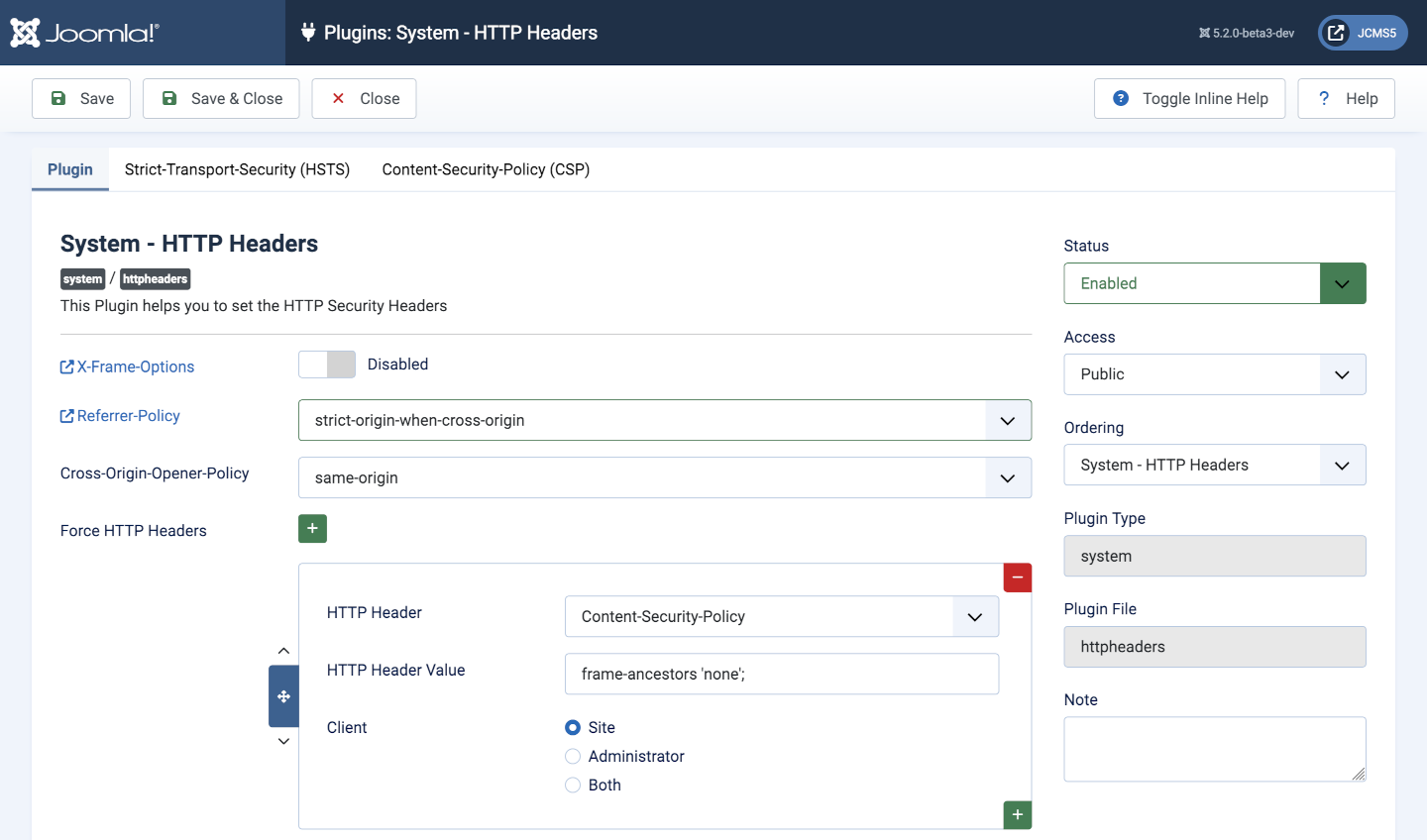
- X-Frame Options This is enabled by default but the documentation says that is deprecated and a frame-ancestors policy should be used instead.
- Referrer-Policy The default is strict-origin-when-cross-origin.
- Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy The Joomla default value is
same-origin. - Force HTTP Headers There are no forced headers set by default. This is where an alternative to X-Frame Options can be specified. The value of
Content-Security-Policycan be one of:'none''self' https://www.example.org;'self' https://example.org https://example.com https://store.example.com;
Using the Force HTTP Headers subform you can also force the following headers:
- Content-Security-Policy
- Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only
- Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy
- Expect-CT
- Feature-Policy & Permissions-Policy
- NEL (Network Response Logging)
- Referrer-Policy
- Report-to
- Strict-Transport-Security
- X-Frame-Options
Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) tab
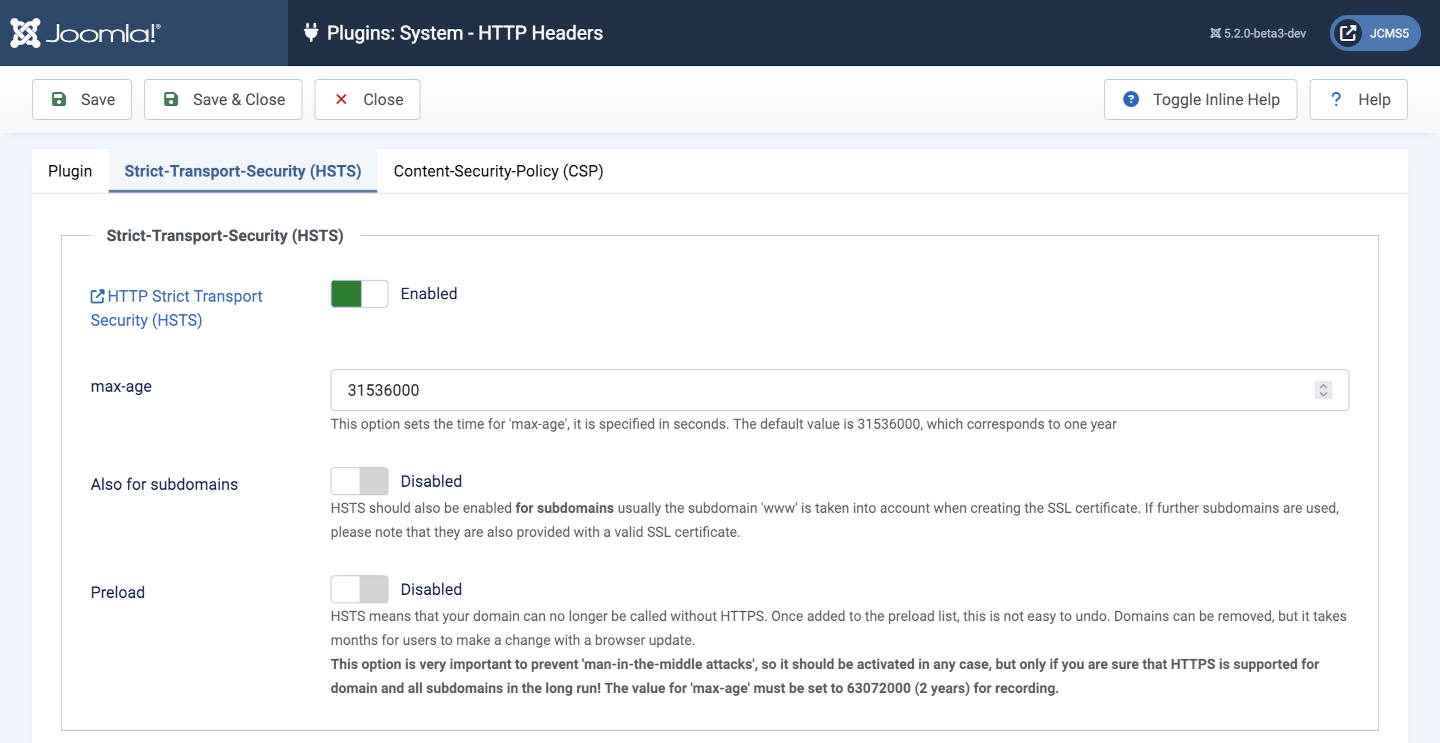
Use the Toggle Inline Help button for information on each parameter. Illustrated reference:
Form to check or set HSTS preload status and eligibility
Content-Security-Policy (CSP) tab
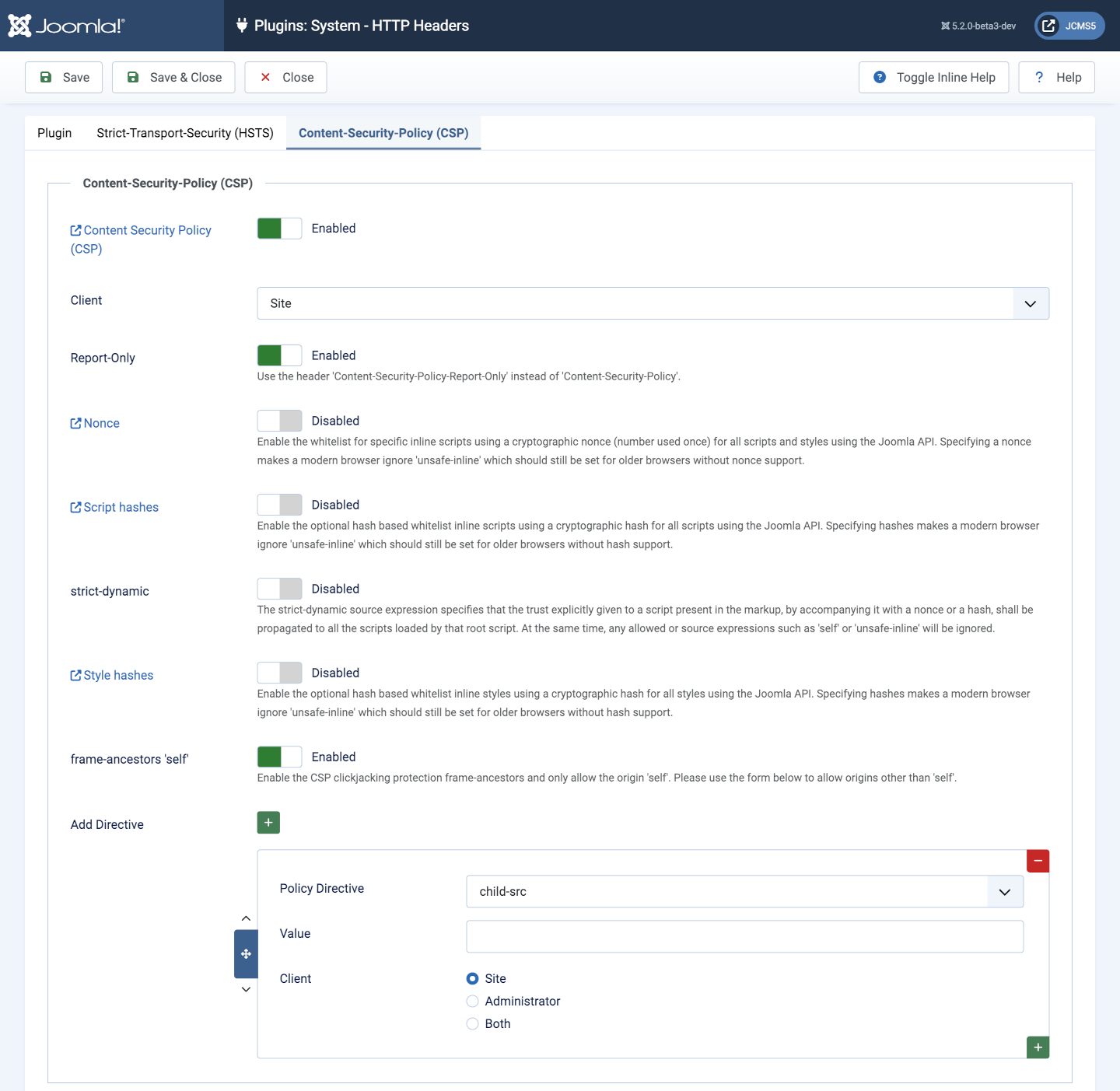
Once enabled you can set the client where you want to enforce the configured CSP, allowing you to set set site, administrator or both. A CSP should be applied to both frontend and backend. Illustrated references:
- Content Security Policy
- Nonce
- Script and Style Hashes
- Policy Directive src descriptions are available in the menu of this page.
The final option called Add Directive allows you to configure the allowlist per directive as you need them. For example, for the script-src directive the Value filed should contain the origins you want to allow to load scripts from.
Notes
When you have configured some HTTP Security Headers directly on the server, there may be double entries.
Check the output of your HTTP Headers in the browser console. In Google Chrome or Firefox: Inspect → Network → the output under Headers. You can than disable the headers that cause double entries. Also check the console of your browser for possible errors.
Extension Developers
The big advantage of a Content Security Policy occurs when the Header blocks all inline JavaScript and inline CSS affecting JavaScript event handlers via HTML attributes. With browser protection enabled inline JavaScript and inline CSS is blocked for extensions also. That protection is not enabled by default but can be enabled by users.
Where inline JavaScript and CSS are required, nonce and hash support are included in the Document APIs. When used, the core will make sure they are whitelisted but will still block malicious code.
Important notes for Extension Developers
Starting with Joomla 4.0 the Content Security Policy:
- is shipped with the core.
- is disabled by default.
- can be enabled by site administrators.
- it is strongly recommended that your extension frontend and backend work with the Content Security Policy enabled.
With strict Content Security Policy enabled the following features will be blocked:
- The execution of JavaScript via the HTML event handlers (onXXX handlers like onClick and similar).
- The execution of in-page JavaScript not passed to the page via the Document API.
- The execution of JavaScript code injected into DOM APIs such as eval().
- The usage of inline in-page CSS not passed to the page via the Document API.
- The usage of inline CSS using the HTML style attribute.
To get your extensions work even with a strict Content Security Policy enabled, the easiest way is to use the Document API to apply your inline JavaScript and CSS. See the examples below.
Adding JavaScript using the Joomla API
use Joomla\CMS\Factory;
/** @var Joomla\CMS\WebAsset\WebAssetManager $wa */
$wa = Factory::getApplication()->getDocument()->getWebAssetManager();
// Add JavaScript from URL
$wa->registerAndUseScript('com_example.sample', 'https://example.org/sample.js', [], ['defer' => true]);
// Add inline JavaScript
$wa->addInlineScript('
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function(event) {
alert("An inline JavaScript Declaration");
});
');
Adding CSS using the Joomla API
use Joomla\CMS\Factory;
/** @var Joomla\CMS\WebAsset\WebAssetManager $wa */
$wa = Factory::getApplication()->getDocument()->getWebAssetManager();
// Add Style from URL
$wa->registerAndUseStyle('com_example.sample', 'https://example.org/sample.css');
// Add inline Style
$wa->addInlineStyle('
body {
background: #00ff00;
color: rgb(0,0,255);
}
');
Additional resources
- CSP Cheat Sheet
- Content Security Policy - An Introduction
- Security Headers is a part of Probely and was originally created by Scott Helme! It is a free and easy to use tool designed to help you better deploy and understand modern security features that are available for your website.
- CSP Evaluator
- Web Fundamentals Content Security Policy
- Google's CSP Documentation
- CSP Is Dead, Long Live CSP! On the Insecurity of Whitelists and the Future of Content Security Policy
- web.dev search for Security